August 7, 2024
How Payment History Affects Your Credit Score & Financial Future

Your payment history isn't just a list of transactions—it's the most crucial factor influencing your FICO credit score. Discover how on-time payments can unlock financial opportunities, while late payments can create obstacles. Learn the specifics of what impacts your payment history, how long it stays on your record, and actionable tips to improve your credit health. Whether you have a pristine payment history or are looking to rebuild, understanding this critical factor is key to securing a brighter financial future. Read on to take control of your credit journey!
How Does Payment History Impact Your Credit Score?
Paying bills on time may seem like a simple task, but it holds immense power over your long-term financial success. Your payment history – a record of how consistently you've paid debts – is one of the most crucial factors influencing your credit score. Making payments on time contributes to a higher score, paving the way for lower interest rates, easier loan approvals, and many other financial benefits. Conversely, late or missed payments can negatively affect your credit score.
Let's delve into the intricacies of payment history and how it impacts your credit score.
What is Payment History?
Your credit reports contain a wealth of information, including your payment history. The payment history portion details your track record of making or missing payments on various credit accounts.
Payment history can help or hurt your credit score — it all depends on what reporting agencies gather from your payment activity.
Aspects of your payment history that can help your credit score:
- Consistent On-Time Payments: Establishing a pattern of on-time payments across multiple credit accounts.
- Lengthy Positive History: Demonstrating responsible credit management over an extended period.
- Diverse On-Time Payments: Successfully managing different types of credit (credit cards, loans, etc.).
- Absence of Recent Negative Marks: Avoiding late payments, especially in the recent past.
Things in your payment history that can hurt your credit score:
- Late Payments: Missed or late payments are major negative marks.
- Collections Accounts: If a debt goes unpaid for an extended period, it may be sent to collections, severely damaging your credit.
- Bankruptcy: Filing for bankruptcy has a long-lasting negative impact on your credit score.
- Foreclosures and Repossessions: Losing a home or having a car repossessed due to non-payment are also very negative marks.
The degree to which these factors affect your credit score varies based on the severity and frequency of the negative events, as well as your overall credit profile.
For example, a single late payment might not actually lead to a drastic drop in your credit score if you have an otherwise lengthy credit history filled with on-time payments. Multiple accounts with late payments or falling far behind on a single bill could compound the problem.
What Types of Accounts Are Included?
Credit reporting agencies typically include payment history on the following types of accounts:
- Credit cards
- Retail/department store cards
- Installment loans
- Mortgage loans
- Other finance accounts, such as lines of credit
FICO, a leading credit scoring model, considers seven specific components within your payment history to calculate your score.
- Payment information on the above types of accounts
- How far overdue current or past delinquent payments are
- Amount owed on current delinquent accounts
- Number of past due items and adverse public records, such as bankruptcies
- Public bankruptcy records
- How much time has passed since delinquencies, adverse public records or collection items
- Number of accounts in good standing
Why is Payment History So Important?
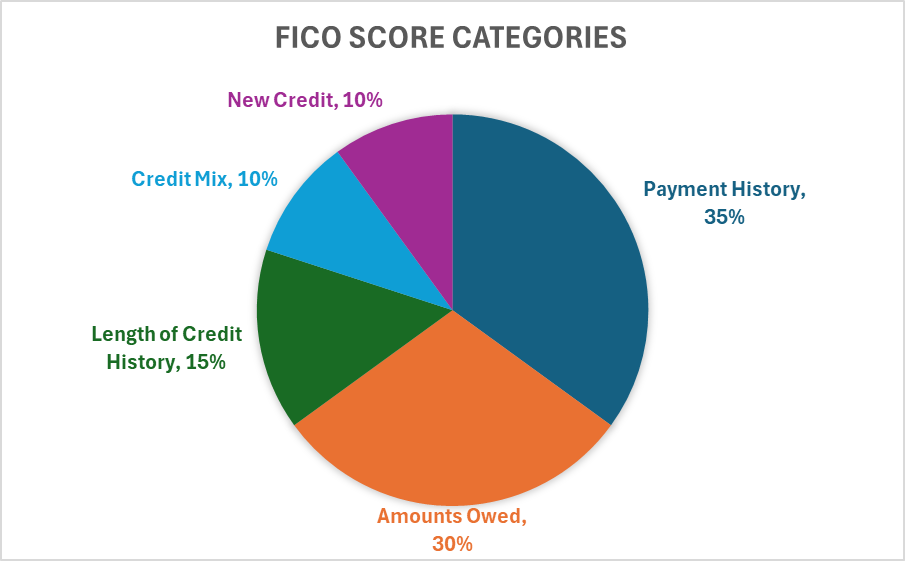
Payment history is the cornerstone of a strong credit score. It makes up a whopping 35% of your FICO score calculation, making it the single most influential factor.
How Late Is “Late”?
Most creditors don’t report you as late the day you are overdue. Creditors only report accounts that are at least 30 days past due. However, if you bring the account current before it is reported to the bureau, the lender may not report it. The important thing is to work with your lender.
How Long Does Payment History Stay on Your Credit Report?
Information can stay in your payment history for seven to ten years. The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) is a federal law that governs how long certain information can remain in your credit report. Once an item drops off your report, it will no longer be a ranking factor in your credit scores.
Most negative items fall off your credit report seven years after they’re reported to a credit bureau. If you were late multiple months in a row, the timeline starts with the first late payment, and the entire sequence will be removed after seven years. One exception is bankruptcies, which may remain on your credit report for up to 10 years, depending on the type of bankruptcy.
While this may seem daunting, remember that older entries typically have less impact than recent ones.
3 Tips to Improve Payment History
There are several actions you can take that may help you improve your payment history and credit scores:
- Open Accounts Wisely: When seeking credit, choose accounts that report to credit bureaus.
- Prioritize On-Time Payments: Even minimum payments made on time can positively influence your credit score.
- Use Credit Responsibly: Keep credit card balances low and pay them off in full each month.
Payment History and RISE Loans
At RISE, we understand that everyone's financial journey is unique. We work with borrowers who may have mixed payment histories and are committed to helping them rebuild their credit. By reporting payment activity to major credit bureaus, we empower our customers to establish a positive credit track record.
Your payment history is a powerful tool for shaping your financial future. By understanding its significance and adopting responsible financial habits, you can build a strong credit score that opens doors to better financial opportunities.
The content provided is for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute financial or legal advice. RISE is not acting as a credit counseling or repair service, debt consolidation service, or credit services organization in providing this content. RISE makes no representation about the reliability or suitability of the information provided – any action you take based on this content is at your own risk.
Trending Articles
March 7, 2022





